-
Contact
Sales & Customer Service
0800 612 6537 support@safelincs.co.uk Live ChatDelivery Enquiries
0800 077 6149 - Resources
Fire & Safety Solutions
CALL OUR TEAM NOW 0800 612 6537
Also FREE from UK mobiles
Free Delivery
on 100s of Products
Live Chat - Online
Instant help & Advice
Trade Discounts
and exclusive pricing
0% Credit Available
Open an account now
5 Star Customer Feedback
Fire Extinguisher Types and Fire Classes
Fire extinguishers are available in different sizes and contain different media. Care should be taken to select the correct fire extinguisher for the environment or premises based on the types of risk identified at the site, the size and layout of the building and the people using the site. The provision of fire extinguishers in any commercial premises is governed by the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 (RRO). The type of extinguishers placed in any building should comply with this legislation whilst also ensuring that it is suitable and sufficient to protect against the fire risks and building users identified in the fire risk assessment.
What are the main fire extinguisher types?
There are six main types of fire extinguisher:
A relatively new type of fire extinguisher has also been developed to tackle lithium-ion battery fires and uses AVD (Aqueous Vermiculite Dispersion) to cool the fire and prevent re-ignition.
Choosing the correct fire extinguisher type to put out a fire is important as each extinguisher is designed and certified to be used on different types of fire (or fire classes).
In accordance with the European manufacturing standard BS EN3, each fire extinguisher type is recognisable by it’s coloured label and clear identification on the front of the extinguisher body. The suitability of each extinguisher is also clearly detailed on the front using the fire class symbols.
Fire classes
The fire classification system is designed to categorise fires into groups based on the type of fuel involved. Each of the fire classes is represented by a letter of the alphabet (with the exception of electrical which are simply referred to as "electrical fires") and an icon. This helps users to select an appropriate fire extinguisher in the event of a fire.
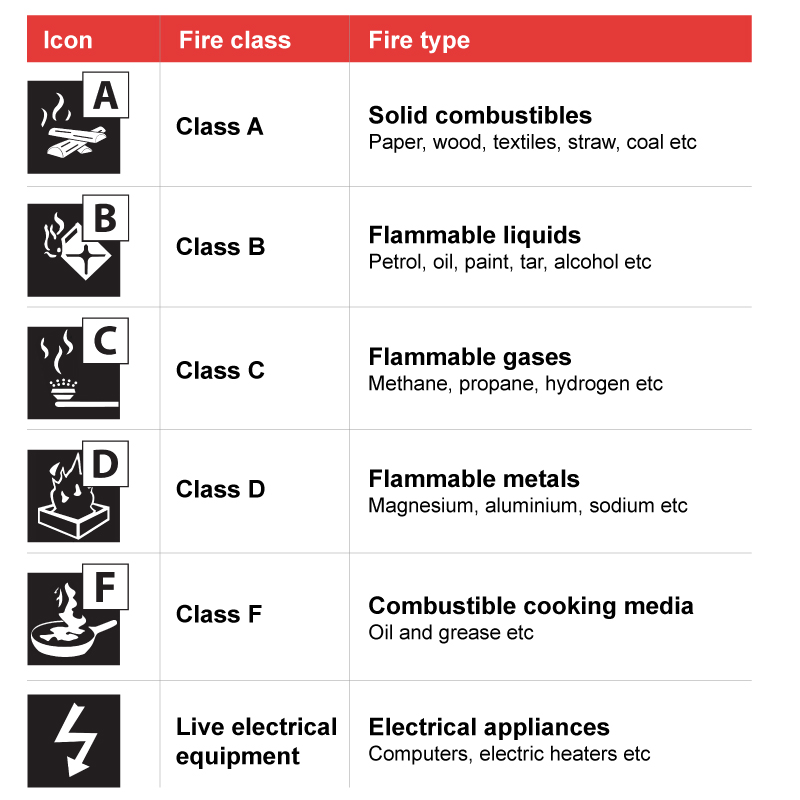
| Fire Class Icon | Fire Class | Type of Fire / Fuel |
|---|---|---|
 |
Class A Fires | Solid Combustibles
Wood, textiles, straw, paper, coal etc. |
 |
Class B Fires | Flammable Liquids
Petrol, oils, paints, tar, ether, alcohol, stearin and paraffin. |
 |
Class C Fires | Flammable Gases
Methane, propane, hydrogen, acetylene, natural gas and city gas. |
 |
Class D Fires | Flammable Metals
Magnesium, aluminium, lithium, sodium, potassium and their alloys. |
 |
Class F Fires | Combustible Cooking Media
Cooking oil and grease |
 |
Electrical Fires | Electrical Appliances
Computers, electrical heaters, stereos, fuse boxes etc. |
Fire extinguisher types and their uses
Each type of fire extinguisher is suitable for different fire classes and it is essential that you purchase suitable extinguishers to cover the risks that exist at your premises. Always refer to your fire risk assessment and results of your fire extinguisher survey when purchasing extinguishers.
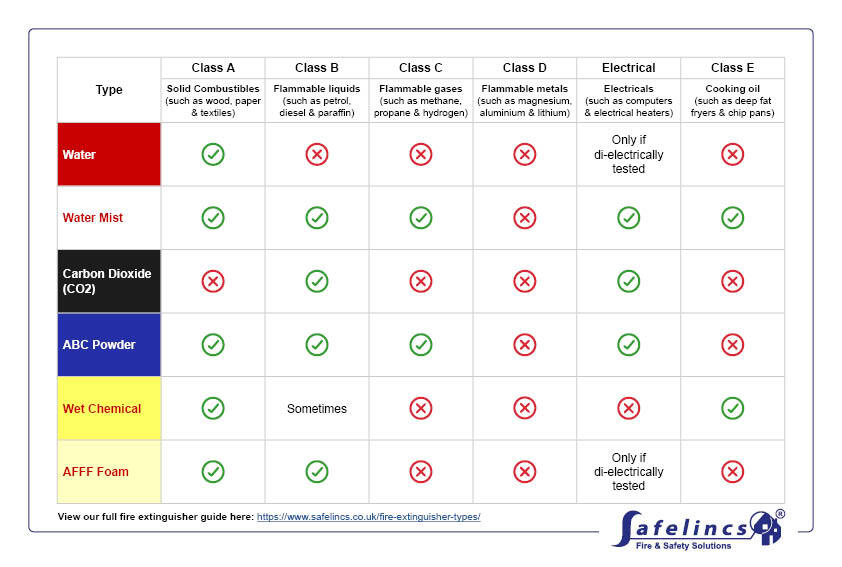
| Type | Class A | Class B | Class C | Class D | Electrical | Class F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid combustibles (such as wood, paper & textiles) |
Flammable liquids (such as petrol, diesel & paraffin) |
Flammable gases (such as methane, propane & hydrogen) |
Flammable metals (such as magnesium, aluminium & lithium) |
Electricals (such as computers & electric heaters) |
Cooking oil (such as deep fat fryers & chip pans) |
|
| Water | Only if di-electrically tested | |||||
| Water Mist | * | |||||
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | ||||||
| ABC Powder | ||||||
| Wet Chemical | Sometimes | |||||
| AFFF Foam | Only if di-electrically tested |
*We do not recommend using water mist on anything above a 5F rated fire (this is equivalent to an average domestic deep fat fryer).
Water fire extinguishers
How to identify a water fire extinguisher
Water fire extinguishers have a red label and a class A rating. Often the least expensive extinguisher, these extinguishers are not toxic or harmful to the environment as they contain only water.
What type of fire can I use a water fire extinguisher on?
They are suitable for fighting fires involving solid combustibles such as wood, paper and fabric. A few models are also safe on electrical equipment if di-electrically tested. Otherwise, care must be taken near electrical equipment.
- Wood, coal and straw
- Paper and cardboard
- Fabric
- Some plastics
- Rubber
Don't use on: Water extinguishers should never be used to extinguish class F, D or B fires and in some cases could exacerbate the situation if discharged on one of these types of fire.

Where can a water extinguisher be used?
- Offices
- Schools
- Shops
- Hospitals
- Public buildings
Water is often paired with CO2 fire extinguishers to cover all common fire risks.
How do water fire extinguishers work?
Water fire extinguishers work by soaking the fire and materials in water, removing the heat and cooling the fire significantly so it can no longer burn.
Fire Classification
Water mist fire extinguishers
How to identify a water mist fire extinguisher
Water mist fire extinguishers have a white label and are highly effective on class A, B, C and live electrical equipment. These versatile extinguishers contain only de-ionised water but are more effective on a broad range of fire types when compared to standard water extinguishers due to the way the media is dispensed.
What type of fire can I use a water mist fire extinguisher on?
- Solid combustibles eg. Wood, coal, paper, fabric etc.
- Flammable liquids eg. Petrol, oils, paint, alcohol, parafin etc.
- Flammable gases eg. Propane
- Small quantities of cooking oils and grease
- Live electrical equipment up to 1000v from a distance of 1m
Don't use on: Commercial deep fat fryers (large class F fires), flammable metals (class D)
Any water mist extinguishers displaying the live electrical equipment symbol on the front have been di-electrically tested in accordance with BS EN3 and are suitable for use on live electrical equipment up to 1000 volts at a distance of 1m. Some water mist extinguishers are also certified for class F fires, however we do not recommend using water mist on anything above a 5F rated fire (equivalent to a domestic deep fat fryer).

Where can a water mist extinguisher be used?
Due to their versatility, water mist extinguishers are ideally suited to any environment that contains mixed fire risks.
- Offices
- Schools
- Shops
- Hospitals
- Public buildings
Many of these settings would usually require a water and CO2 extinguisher to cover class A fires and fires involving electrical equipment. Water mist can cover both of those fire risks effectively, negating the need for two extinguishers.
How do water mist fire extinguishers work?
Water mist extinguishers have a superfine spray nozzle that dispenses microscopic droplets of de-ionised water. The mist curtain reduces the supply of oxygen to the fire and cools the materials, preventing reignition. Containing only de-ionised water, water mist is an environmentally friendly media and leaves no messy residue to clean up after discharge.
Fire Classification
CO2 fire extinguishers
How to identify a CO2 fire extinguisher
CO2 fire extinguishers are identified by their black label and usually have a frost-free horn that protects the user from freeze-burns when discharged.
What type of fire can I use a CO2 extinguisher on?
- Fires involving electrical equipment
- Flammable liquids (class B)
They are predominately used on fires involving live electrical equipment, as CO2 is not a conductor. In addition, CO2 extinguishers don’t leave behind any harmful residue so can often be discharged on expensive electrical equipment without causing damage. They were originally designed for use on flammable liquid fires and therefore many have a class B fire rating.
Don't use on: Solid combustibles due to a risk of re-ignition.

Where can a CO2 extinguisher be used?
- Server rooms
- Any room containing a large amount of large electrical equipment
CO2 extinguishers are also commonly found in offices, warehouses, schools or retail premises paired with water of foam extinguishers. They have traditionally been specified to cover electrical fire risks in these locations but as there are now extinguishers that are both di-electrically tested and cover class A risks, this pairing is not usually necessary.
CO2 extinguishers contain only carbon dioxide gas and care should be taken when discharging them as there is a risk of asphyxiation if used in confined spaces. Frostbite can also occur if the discharged CO2 comes into contact with the users skin (the frost-free horn is designed to prevent this).
How to CO2 extinguishers work?
CO2 extinguishers work by cutting off the oxygen supply from the fire and effectively suffocating it. CO2 extinguishers can pose a risk of re-ignition as they are not effective as a coolant in the way that water is, and if discharged on class A or class F fires, could actually make the fire worse.
Fire Classification
Dry powder fire extinguisher
How to identify dry powder extinguishers
Dry powder extinguishers have a blue label and will feature the word 'Powder' on the front.
What type of fire can a dry powder extinguisher be used on?
They are versatile and can be used on:
- Solid combustibles eg. Wood, coal, paper, fabric etc.
- Flammable liquids eg. Petrol, oils, paint, alcohol, parafin etc.
- Flammable gases eg. Propane
- Fires involving live electrical equipment

Where can a powder extinguisher be used?
- Construction sites
- Garage forecourts
- Vehicles & machinery
Powder extinguishers are ideally suited to outdoor locations as there is a risk of inhalation when discharging them indoors. They are also difficult to clean up when discharged and can cause damage to soft furnishings.
How do powder fire extinguishers work?
Powder extinguishers (also referred to as dry powder or ABC powder) contain mono-ammonium phosphate which is mixed with other powders. They work by smothering the fire which creates a barrier between the fuel and the oxygen.Fire Classification
Wet chemical extinguishers
How to identify a wet chamical fire extinguisher
Wet chemical fire extinguishers (also known as class F extinguishers) have a yellow label and are designed specifically for use on fires involving combustible cooking media such as burning oil and fat.
What type of fire can I use a wet chemical fire extinguisher on?
- Solid combustibles eg. Wood, coal, paper, fabric etc. (class A fires)
- Cooking oils and grease (class F fires)
Some are also designed for use on class B fires (petrol, diesel, paint, paraffin etc) and fires involving live electrical equipment as indicated on the front of the extinguisher body.
Dont use on: Class C (flammable gases) and class D (flammable metals) fires.

Where can a wet chemical fire extinguisher be used?
- Commercial kitchens
- Deep fat fryers
How do wet chemical fire extinguishers work?
Containing potassium salts, these extinguishers work by creating a soapy barrier between the fire and the oxygen. This cools the fire and prevents reignition. This type of extinguisher has a special lance applicator nozzle that allows the user to gently dispense the media from a suitable distance. Normal water-based extinguishers with large droplets would cause an 'explosion' of steam and carry burning oils and fats from the container. Equally, a CO2 extinguisher's jet would carry burning oil out of the container and also would have insufficient cooling effect to stop re-ignition.
Fire Classification
Foam fire extinguishers
Foam fire extinguishers are identified by their cream label and are designed for class A and B fires plus in some cases fires involving electrical equipment. There are a number of different types of foam fire extinguishers and some are now classified as hazardous to human health and the environment. Foam extinguishers are water-based and contain chemicals that form a ‘frothy agent’. The foam cools and smothers the fire, extinguishing it and preventing reignition.

Foam extinguisher uses
- Offices
- Schools
- Shops
- Hospitals
- Public buildings
AFFF foam
This type of foam extinguisher contains toxic fluorine compounds (PFAS) which is harmful to humans and the environment. AFFF foam extinguishers are due to be phased out by law from 2025 and Safelincs have taken the decision to discontinue the sale of this type of extinguisher.
AFFF foam extinguishers are commonly found in many premises across the UK including offices, schools, warehouses, shops and public buildings. The disposal of this type of media is tightly controlled due to its harmful nature.
Fluorine-free foam
Recently, manufacturers have begun to replace AFFF foam extinguishers with fluorine-free foam extinguishers. This type of fire-fighting foam is versatile in application but is a more environmental choice, being free from the harmful PFAS chemicals contained in AFFF foam. Fluorine-free foams can be used on class A and B fires as well as being di-electrically tested for use on electrical equipment.
Fire Classification

Service-Free Fire Extinguishers
P50 extinguishers are a relatively new type of fire extinguisher and provide an alternative to steel extinguishers that are more durable and easier to maintain. With a plastic outer casing and super-strong inner core, this type of extinguisher will not corrode and does not require annual servicing from an external technician. With twice the lifespan of a traditional steel extinguisher, P50 service-free extinguishers are 100% recyclable and offer an environmental option. They have a low-carbon manufacture process and offer significant cost savings over their long lifespan.
P50 extinguishers are available in a range of media including water mist and eco-foam. They have a 10-year warranty and excellent fire-fighting capability. Find out more about this type of extinguisher on our P50 information guides.
Still not sure which type of fire extinguisher you need?
Read our extinguishers by location and extinguishers for vehicles guides for help choosing the correct extinguishers for your requirements.
Or, contact our friendly team on 0800 612 6537 or email support@safelincs.co.uk for help choosing a suitable extinguisher for your location.
Reviewed: 09/07/2024 (doc:2 V1.7). Our articles are reviewed regularly. However, any changes made to standards or legislation following the review date will not have been considered. Please note that we provide abridged, easy-to-understand guidance. To make detailed decisions about your fire safety provisions, you might require further advice or need to consult the full standards and legislation.



















