-
Contact
Sales & Customer Service
0800 612 6537 support@safelincs.co.uk Live ChatDelivery Enquiries
0800 077 6149 - Resources
Fire & Safety Solutions
CALL OUR TEAM NOW 0800 612 6537
Lines open today 8am - 6pm
FREE Delivery
on marked products
Live Chat - Online
Instant help & Advice
Trade Discounts
and exclusive pricing
0% Credit Available
Open an account now
5 Star Customer Feedback
Semi-Automatic Defibrillators
Primarily designed to be used by medical staff or responders with previous training, semi-automatic defibrillators rely on the user to administer the shock once the device has analysed the patient and deemed a shock to be necessary. Due to the human intervention required to initiate the shock, these devices include safeguards meaning that even untrained personnel are able to use them without the risk of accidentally causing harm.
Read our defibrillator buying guide for more information on the types of defibrillators and their features.
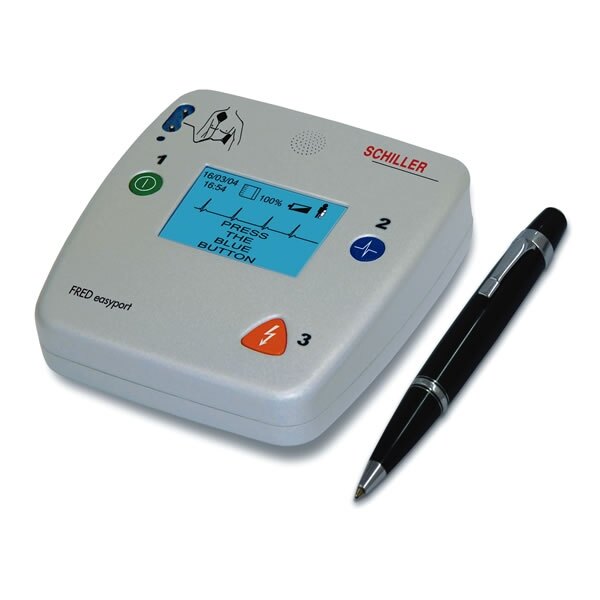
Schiller FRED Easyport Pocket Defibrillator - Semi-Automatic
The FRED Easyport from Schiller is the world's smallest portable defibrillator. At less than half a kilo, the FRED Easyport is small enough and lightweight enough to fit into a bag or coat pocket, while also meeting the technical requirements of a standard size unit.
- Semi-automatic operation
- Defibrillator warranty: 1 year
- Battery stand-by life: 5 years
- Electrode pad life: 2 years
HeartSine Samaritan PAD 350P Defibrillator with Carry Case - Semi-Automatic
Produced by a world leader in defibrillators for public access , the HeartSine Samaritan PAD 350P semi-automatic AED comes with a 10 year warranty.
- Semi-automatic operation
- Defibrillator warranty: 10 years
- Battery stand-by life: 4 years
- Electrode pad life: 4 years
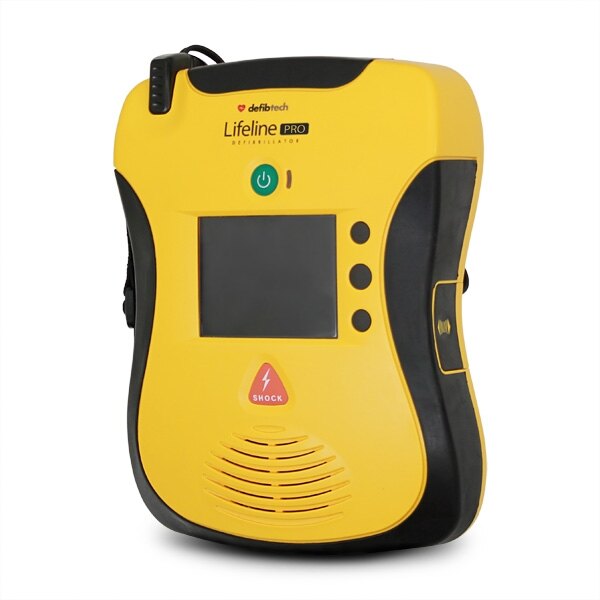
Defibtech Lifeline Pro Defibrillator - Semi-Automatic
Configurable in 3 operating modes, the Defibtech Lifeline Pro is a life saving semi-automatic defibrillator, for non-diagnostic ECG monitoring or with manual override facility.
- Semi-automatic operation
- Defibrillator warranty: 8 years
- Battery stand-by life: 4 years
- Electrode pad life: 2 years
Physio-Control Lifepak 1000 Defibrillator - Semi-Automatic
The Physio-Control Lifepak 1000 semi-automatic defibrillator maximises hands-on CPR time and is able to escalate shock energy levels during treatment. When used with the 3-lead ECG cable (sold separately), the ECG mode can be enabled.
- Semi-automatic operation
- Defibrillator warranty: 5 years
- Battery stand-by life: 5 years
- Electrode pad life: 18 months
HeartSine Samaritan PAD 350P Defibrillator with Indoor Cabinet and AED Responder Kit
The HeartSine Indoor Bundle includes a HeartSine Samaritan PAD 350P Semi-Automatic AED with Carry Case, Indoor Wall Cabinet and an AED Responder Kit.
- Ideal for schools, offices, hospitals and businesses
- Includes a HeartSine Samaritan PAD 350P Semi-Automatic Defibrillator
- Includes an Internal Wall Cabinet and AED Responder Kit
- The HeartSine 350P features a 10 year warranty
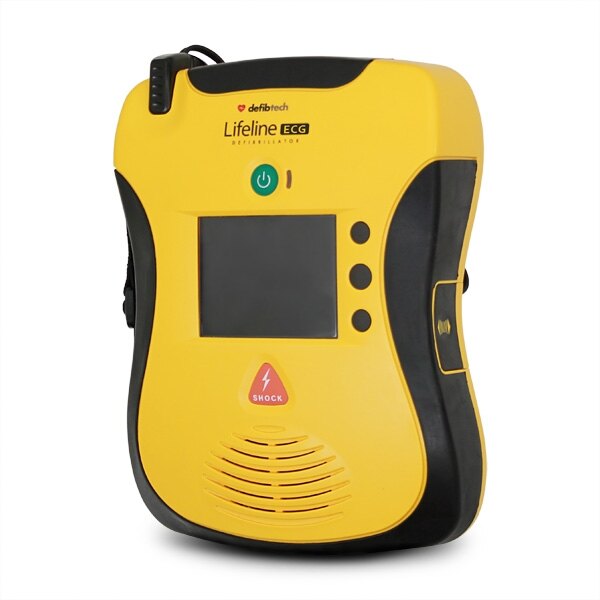
Defibtech Lifeline ECG Defibrillator - Semi-Automatic
Made for use by medical professionals, the Defibtech Lifeline ECG defibrillator displays critical patient data including ECG, heart rate, number of shocks delivered and elapsed rescue time.
- Semi-automatic operation
- Defibrillator warranty: 8 years
- Battery stand-by life: 4 years
- Electrode pad life: 2 years
Physio-Control Lifepak 1000 ECG Defibrillator (with Manual Operation) - Semi-Automatic
The Lifepak 1000 defibrillator with ECG display from Stryker (formerly Physio-Control) allows the patient's heart rhythm to be monitored by medical professionals who can then determine if and when a shock is to be administered.
- Semi-automatic operation
- Defibrillator warranty: 5 years
- Battery stand-by life: 5 years
- Electrode pad life: 18 months
Page 2 (27 of 27 Products)